Medium density fiberboard (MDF) has long been a staple material in woodworking and manufacturing, known for its versatility and affordability. However, the introduction of laser cutting technology has taken the possibilities and precision of MDF processing to new heights. Laser cutting MDF uses a laser beam to precisely cut, engrave or etch designs into medium density fiberboard.
In this blog, we will explain how to laser cut MDF, answer common questions about the process, and explore the fusion of traditional woodworking materials with cutting-edge laser technology.

In this article:
Part 1: What Is MDF?
Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF) is an engineered wood product made from wood fibers, wax, and resin, compressed at high temperatures to create a dense and uniform board.
1. Composition of Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF)
- Wood fibers: Sourced from various hardwoods and softwoods.
- Wax: Enhances water resistance and binding of fibers.
- Resin: Typically a urea-formaldehyde or melamine-formaldehyde resin, providing cohesion and stability.
2. Properties and Characteristics of MDF
- Density: Medium density, as the name suggests, falls between that of hardwood and softwood. Uniform density throughout the board, contributing to consistent cutting results.
- Smooth Surface: MDF has a smooth and flat surface, ideal for intricate laser engravings. Consistent texture facilitates precise cutting and detailed designs.
- Stability: Minimal expansion and contraction due to changes in temperature or humidity. Maintains shape and integrity over time.
3. Advantages and Disadvantages of MDF
Advantages of MDF:
- Affordability: Cost-effective compared to solid wood.
- Versatility: Suitable for a variety of applications.
- Smooth Surface: Ideal for painting, laminating, and intricate laser work.
Disadvantages of MDF:
- Susceptibility to Moisture: Not recommended for high-moisture environments.
- Weight: Denser than some alternative materials.
- Safety Hazards: Generate toxic gases during laser cutting, requiring additional protective measures.
Part 2: How to Laser Cut MDF - Step by Step Guide
Laser cutting MDF involves a combination of precise technology and thoughtful design considerations. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you navigate the process:
Step 1. Preparation
Choose the Right Laser Cutter:
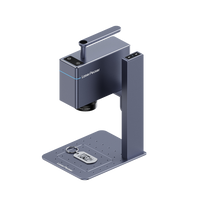
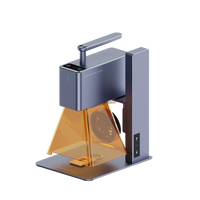
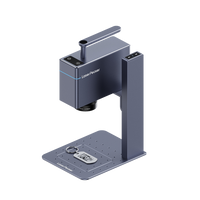
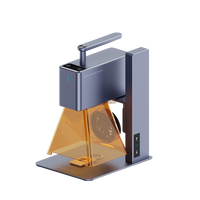
Find a laser cutter suitable for MDF cutting, such as LaserPecker LX. It can laser cut MDF, Plywood, Wood of specific thickness.
Select the Right Type of MDF:
Choose MDF with a smooth and consistent surface for optimal laser cutting results. Consider the thickness of the MDF based on your project requirements.
Step 2. Set Up the Laser Cutting Machine
Calibrate the Laser:
Adjust laser power, speed, and focus settings according to the type and thickness of the MDF. Perform test cuts on scrap material to fine-tune the settings for optimal results.
Secure the MDF:
Place the MDF securely on the laser cutting bed. Use masking tape or other methods to prevent the material from moving during the cutting process.
Step 3. Load and Configure the Design
Design Your Project:
Use vector-based design software to create your design. Ensure the design is compatible with laser cutting parameters (e.g., lines for cutting, different colors for engraving).
Load the Design File:
Import your design file into the laser cutting software. Arrange multiple designs on the cutting bed for efficiency.
Configure Cutting Parameters:
Specify cutting and engraving settings for each element in your design. Double-check the laser settings to ensure they match the requirements of your project.
Step 4. Execute the Laser Cutting
Run a Test Cut:
Before cutting the entire design, run a test cut on a small section of the material to verify settings and make any necessary adjustments.
Start the Cutting Process:
Start the laser cutting machine and observe the process. Ensure proper ventilation and safety measures like laser safety glasses are in place.
Monitor the Cutting Progress:
Keep an eye on the cutting progress to address any issues promptly. Pause or stop the machine if needed.
Step 5. Post-Processing
Remove the Cut Pieces:
Once the cutting is complete, carefully remove the cut pieces from the laser cutting bed.
Inspect and Clean:
Inspect the cut edges for quality. Clean the MDF surface if necessary, removing any residue from the cutting process.
Final Touches:
Sand or finish the edges of the cut pieces for a polished look.
Part 3: Applications of Laser Cut MDF
The marriage of laser cutting technology and Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF) has opened up a world of possibilities in various industries. The versatility and precision offered by laser cut MDF make it an ideal material for a wide range of applications. Here are some notable uses:
1. Home Decor and Furniture:
Intricate Patterns and Designs: Laser cut MDF allows for the creation of detailed patterns, filigree, and ornate designs in furniture and home decor items.
Customized Shelving and Cabinets: Designers can use laser cutting to create unique and personalized shelving and cabinet solutions with intricate detailing.
2. Architectural Models and Prototyping:
Scale Models: Laser cut MDF is employed in architectural model-making for creating detailed and accurate scale models of buildings and landscapes.
Prototyping: Designers and architects use laser cut MDF to quickly prototype and iterate their designs before finalizing larger-scale projects.
3. Signage and Branding:
Precision Lettering and Logos: Laser cut MDF is ideal for crafting precise lettering and logos for signage and branding purposes.
Themed Displays: Retailers and event planners use laser cut MDF to create themed displays for promotional events and storefronts.
4. Educational and DIY Projects:
STEM Education: Laser cut MDF is utilized in educational settings to teach STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) concepts through hands-on projects.
DIY Home Projects: Enthusiasts and hobbyists leverage laser cut MDF for various DIY projects, from decorative wall art to personalized gifts.
5. Art and Craft:
Detailed Artwork: Artists use laser cut MDF to create intricate and detailed artwork, combining traditional artistic techniques with modern technology.
Custom Stencils: MDF stencils cut with precision allow artists to replicate complex patterns and designs in their work.
6. Packaging and Display:
Custom Packaging: Laser cut MDF is employed in the creation of custom packaging solutions for products, adding a touch of uniqueness and branding.
Product Displays: Retailers use laser cut MDF for designing attractive and customized product displays to enhance visual appeal.
Part 4: FAQs about Laser Cut MDF
1. What types of lasers are used for cutting MDF?
Diode lasers are commonly used for cutting MDF. These lasers are efficient at engraving and cutting a wide range of materials, including wood.
2. What thickness of MDF is suitable for laser cutting?
The suitable thickness depends on the laser cutting machine's power and focal length. Generally, MDF with a thickness ranging from 1/8 inch to 1/2 inch is commonly used for laser cutting.
3. Can laser cut MDF be used for outdoor applications?
While MDF itself is not suitable for outdoor use due to its susceptibility to moisture, finished laser cut MDF pieces can be sealed or coated for limited outdoor applications. However, it's recommended to use other materials like plywood for extended outdoor exposure.
4. Is laser cutting MDF environmentally friendly?
The environmental impact depends on the sourcing of MDF and the disposal of waste. Some MDF is made from recycled wood fibers, and laser cutting can be efficient in minimizing material waste if done correctly.
5. Is laser cut MDF suitable for mass production?
Yes, laser cut MDF is well-suited for mass production due to its efficiency and precision. However, factors such as machine capacity and design complexity should be considered.